My son and I were having a picnic in the field when suddenly a little animal dashed past us.
He jumped up in the excitement and shouted, “Look, mom, it’s a rabbit.” On closer inspection, I realized that it was a hare.
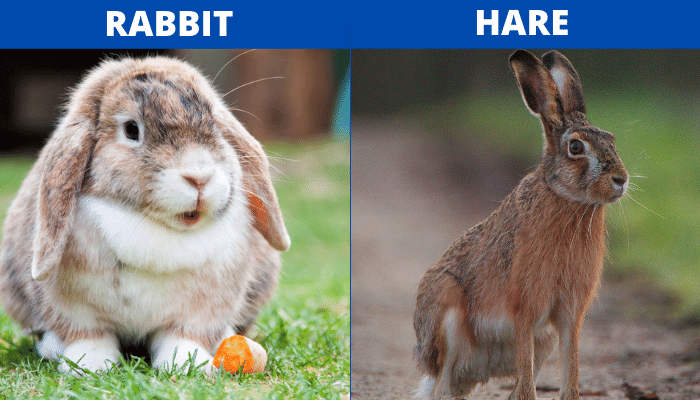
This was the perfect opportunity for us to look at the differences (and a few similarities) between rabbits and hares.
The main difference between rabbits and hares is that they are a different species altogether, but they do belong to the same family (Leporidae).
Rabbits and hares may look very similar (at a glance), but there are some obvious differences in their diet, living environment, physical appearance, and behavior.
For example, rabbits live in burrows underground, while hares can be found in nests made above the ground.
Rabbit vs Hare – How are they Different?
Here’s a list of differences between rabbits and hares:
1. Living Environment
Rabbits and hares have very different needs for their living environments.
Let’s take a look at their different living environments:
Rabbit
Wild rabbits prefer to run and hide from predators, so they like areas with trees, shrubs, and soil where they can tunnel into the ground and make burrows (underground tunnels) with multiple exits to escape.
Meadows, woods, and grasslands make excellent living environments for wild rabbits.
Domestic rabbits do not need to evade predators, so they live in cages, enclosures, or hutches inside or outside your home.
Hare
Hares prefer to sprint away from predators and live in open farmland and grassland areas. They live very nomadic lives and sleep anywhere that’s suitable for them.
A hare will scrape away plants and lie down in the soil, which causes a shallow indentation in the ground known as a form.
They flatten their ears to be undetectable in long grass and are often confused with a pile of hay by predators.
2. Average Body Size
Let’s take a look at the different body sizes of rabbits and hares:
Rabbit
An average domestic bunny weighs about 6 pounds with a body length of approximately 15.79 inches from its nose to its tail.
A wild rabbit weighs about 5 pounds with a body length of about 17 inches from their nose to its tail.
Hare
A hare is generally larger than a rabbit.
An average size hare weighs around 8 pounds, with a body length of about 20 inches from its nose to its tail.
3. Gestation Period
The gestation period between rabbits and hares differs significantly:
Rabbit
Wild rabbits and domestic rabbits can fall pregnant at 12 weeks of age. They have a gestation period of about 30 to 31 days and can conceive at any time of the year.
Hare
Hares have a gestation period of about 42 to 44 days, and a female hare can breed throughout the year.
However, their primary mating season is during spring. Hares can breed from about 6 months of age.
4. Parenting
Let’s take a look at the parenting styles between rabbits and hares:
Rabbit
Baby rabbits (known as kits or kittens) are born blind and naked (altricial); they are helpless and must stay with their mothers for about 8 weeks.
Kits will begin to develop fur and features after about 10 days. Kittens are fully weaned by the time they are about 6 weeks old.
Hare
When a baby hare (leveret) is born, they look like a mini version of their mother. Their eyes are open, and they have a full coat of fur.
They are born independent (precocial) and ready to start running around and fending for themselves after an hour of being born. Baby hares are weaned within 2 to 3 weeks.
5. Limb Length
Another obvious difference between a hare and a rabbit is limb length:
Rabbit
Wild rabbits and domestic rabbits have shorter ears and legs than hares, as they prefer to hide underground from predators rather than run away from them.
Domestic rabbits, however, do have slightly shorter limbs than wild rabbits as they are bred specifically to suit a domestic lifestyle and do not need to evade predators.
Hare
Hares are larger than rabbits and have longer and more powerful hind legs. They also have longer ears than their cousins.
These longer and larger limbs help the hare outrun and evade predators.
6. Dietary Requirements
Rabbits and hares have different dietary requirements:
Rabbit
A wild rabbit’s diet mainly consists of soft plant stems, vegetables with leafy tops such as carrots, and different types of grasses.
A domestic bunny’s diet consists mainly of hay, pellets, a small number of vegetables, and bits of fruit as a treat.
Hare
A hares diet consists of plant roots, shoots, twigs, and bark. They also eat berries, leaves, and flower buds.
7. Predator Evasion Skills
Rabbits and hares have different ways of evading predators, such as:
Rabbit
Rabbits live and hide in burrows or warrens underground to protect themselves and their colony from predators. They also have their litter underground.
When chased by predators, they avoid open areas and run in zig-zag patterns.
Living in a social group is also a great survival technique, as the rabbits alert one another when predators are near.
If a domestic bunny is cornered or feels threatened, it will thump its hind legs and use its teeth and claws to try and fend off predators.
Hare
Hares depend on their ability to run fast to escape predators and don’t hide underground. They are solitary animals and do not live in groups or pairs.
Hares have good hearing, and their fur coats are well camouflaged. If they hear a predator approaching, they freeze in their tracks.
8. Life Span
Let’s take a look at the lifespan of hares and rabbits:
Rabbit
Wild rabbits have a lifespan of about 2 years but sometimes only live to just over a year.
On the other hand, domestic rabbits can live for over 4 years (some even a decade if you look after them well).
Hare
An adult hare can live for about 4 years and rarely live any longer than this.
9. Behavior
Hares and rabbits have different behavioral traits such as:
Rabbit
Rabbits are social animals and live in colonies in underground burrows or warrens. A male rabbit will fight another male to become the dominant male in the colony.
A dominant male will mate with most of the females in the colony. Domesticated bunnies are also social animals and can become depressed if they live on their own.
However, if they have enough attention from their owners and toys to keep them stimulated, they are brilliant and loving animals.
Hare
Hares are solitary, shy animals and prefer to live on their own in nests above the ground. When it’s mating season, they will briefly join a mate to breed.
If a female hare does not want to mate with a male, then she will box him with her paws to warn him off.
Also read: Are Rabbits Smarter Than Dogs?
Rabbit vs Hare – What are the Similarities?
Here are a few similarities between rabbits and hares:
Prey Animals
Rabbits and hares are prey animals, and they run or hideaway to escape predators.
Split Lip
Hares and rabbits have a shared facial feature called a split lip or harelip.
Breed Prolifically
Rabbits and hares breed prolifically and have between 4 to 8 litters a year.
Hare vs Rabbit: Where Did the Terms Originate?
Until the 18th-century, rabbits were known as coneys from the French word conil. The term rabbit comes from the Middle English word rabet.
The word hare comes from the old English word hara, and the dutch word haas.
Rabbit vs Hare FAQs
Can hares breed with rabbits?
Rabbits and hares are from a different species and genus. It’s possible for the two to mate, but it’s impossible for them to breed.
Are rabbits rodents?
Rabbits aren’t rodents. Rabbits are lagomorphs, and unlike rodents, they have an extra pair of incisors, and their skeletal features are different.
Can you eat hare?
You can eat hare meat. Although it’s not as popular as rabbit meat, it’s a gamier and lean type of meat.
Final Thoughts on Rabbits vs Hares
Hopping to conclusions is easy when considering how similar hares and rabbits look, but there are some very distinct differences between the two.
The best way to tell the difference between rabbits and hares is by looking at their body size, diet, and habitat.
There is some truth to the term ‘as mad as a march hare.’
Hares are wild and very skittish, unlike their ‘Bugs Bunny’ cousins, and they can’t be tamed, but rabbits can be domesticated and make great pets.
Other articles you may also like:
